15 Aug The Carotid artery disease and strokes
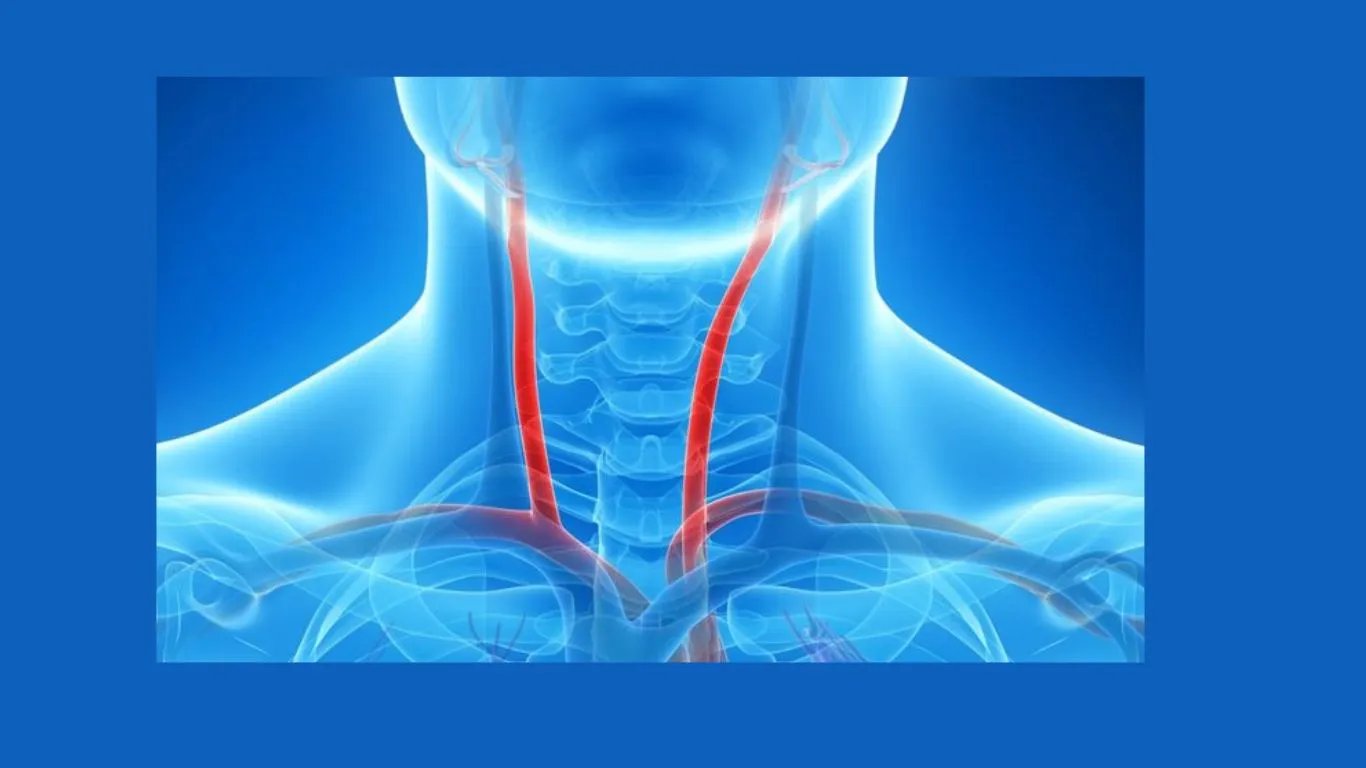
The Carotid artery is the main artery responsible for transporting blood from the heart to the brain, passing through the neck. Carotid artery disease occurs as a result of sclerosis or the buildup of fatty plaques within the artery wall, leading to its narrowing and blockage. Dr. Amir Malkawi, a vascular surgery consultant, will explain in the following article the relationship between Carotid artery disease and strokes.
The Carotid artery disease and strokes
Carotid artery disease is responsible for approximately 20% of strokes. Here is an explanation of the mechanisms through which Carotid artery disease causes strokes:
Artery narrowing
As fatty plaque accumulates in the wall of the carotid artery, it narrows, reducing blood flow to the brain and increasing the risk of stroke.
Plaque detachment from the artery wall
With the increasing size of fatty plaques in the carotid artery wall, they may detach and move through the carotid artery to small arteries within the brain, potentially causing their blockage and cutting off blood supply to parts of the brain. This mechanism is the most common cause of strokes.
Increased risk of blood clot formation
Fatty plaques in the carotid artery may cause cracks or tears in the artery wall, triggering a body response to repair the damage. However, this process may stimulate the release of substances that promote blood clotting and the formation of blood clots that can move to the brain.
Read More: POST-VARICOSE VEIN SURGERY INSTRUCTIONS
Causes of Carotid artery disease leading to stroke
Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of carotid artery disease and increased risk of stroke. There are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing carotid artery disease, including:
- Family history of the disease.
- Aging.
- Genetic factors.
- High blood pressure and poorly controlled hypertension.
- High cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Diabetes.
- Smoking.
- Unhealthy diet.
- Overweight or obesity.
- Lack of physical activity and insufficient exercise.
Symptoms of Carotid artery disease prior to stroke
Unfortunately, most cases of carotid artery disease are not diagnosed until after a stroke occurs because many cases do not present with any clear symptoms in the affected individual. In cases where symptoms of carotid artery disease appear before a stroke, they may include:
- Mental confusion.
- Balance disturbances.
- Blurred vision.
- Movement disorders.
- Dizziness and vertigo.
Symptoms of Carotid artery disease after the formation of a stroke
A range of symptoms and signs appear in individuals with carotid artery disease at the onset of a stroke. Immediate medical emergency consultation is required upon the appearance of these symptoms, including:
- Vision disturbances or seeing floating objects in the visual field.
- Noticing a shadow or dark area in the vision field.
- Sudden loss of vision.
- Difficulty understanding others while speaking.
- Sudden and severe headache.
- Speech stuttering.
- Confusion and disorientation.
- Difficulty walking and muscle coordination disorders.
- Weakness and numbness in limbs, usually affecting one side of the body.
- Drooping on one side of the face.
- Loss of sensation on one side of the body.
Prevention of carotid artery disease and strokes
There are a set of home measures and tips that contribute to preventing carotid artery disease and the associated strokes, or reducing the chances of stroke after diagnosis of the disease, including:
- Abstaining from smoking.
- Controlling harmful cholesterol levels in the blood and raising levels of good cholesterol.
- Managing blood sugar levels.
- Maintaining ideal weight or losing weight in cases of obesity.
- Following a healthy diet that includes adequate amounts of fruits and vegetables and limiting salt intake.
- Engaging in regular physical activity and exercise.
- Managing blood pressure levels.
- Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan for managing any chronic conditions.
References:
[2]-https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/carotid-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20360519
[3] – https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/carotid-artery-disease
[4] – https://www.verywellhealth.com/carotid-artery-disease-7693259
[5]-https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16845-carotid-artery-disease-carotid-artery-stenosis
[6]-https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/c/carotid-artery-disease.html