17 Sep What causes blood clotting in the heart?
Blood clotting is the process where blood changes from a liquid to a solid state. It’s a natural and defensive process in the body that helps stop bleeding in normal circumstances. However, certain health issues can lead to the formation of blood clots within the bloodstream in a manner that exceeds normal needs. This, in turn, can lead to serious health complications such as heart attacks and strokes, as blood clot formation can block vital arteries supplying organs like the heart and brain.
There are cases where blood clots form in the heart, and Dr. Amir Malkawi, a vascular surgery consultant, will explain in the following article the causes and risk factors of blood clotting in the heart.
Causes of Blood Clotting in the Heart
Blood clots form in the heart due to factors that impede blood flow in the cardiac blood vessels, narrow the blood vessels, or affect the body’s blood clotting rate. Other causes include structural heart problems, where blood clotting in the heart can lead to blockages in the coronary arteries supplying the heart muscle, thus halting the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the heart.
There are several reasons that contribute to blood clotting in the heart, including:
Arteriosclerosis (Atherosclerosis)
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common causes of blood clotting in the heart. It leads to:
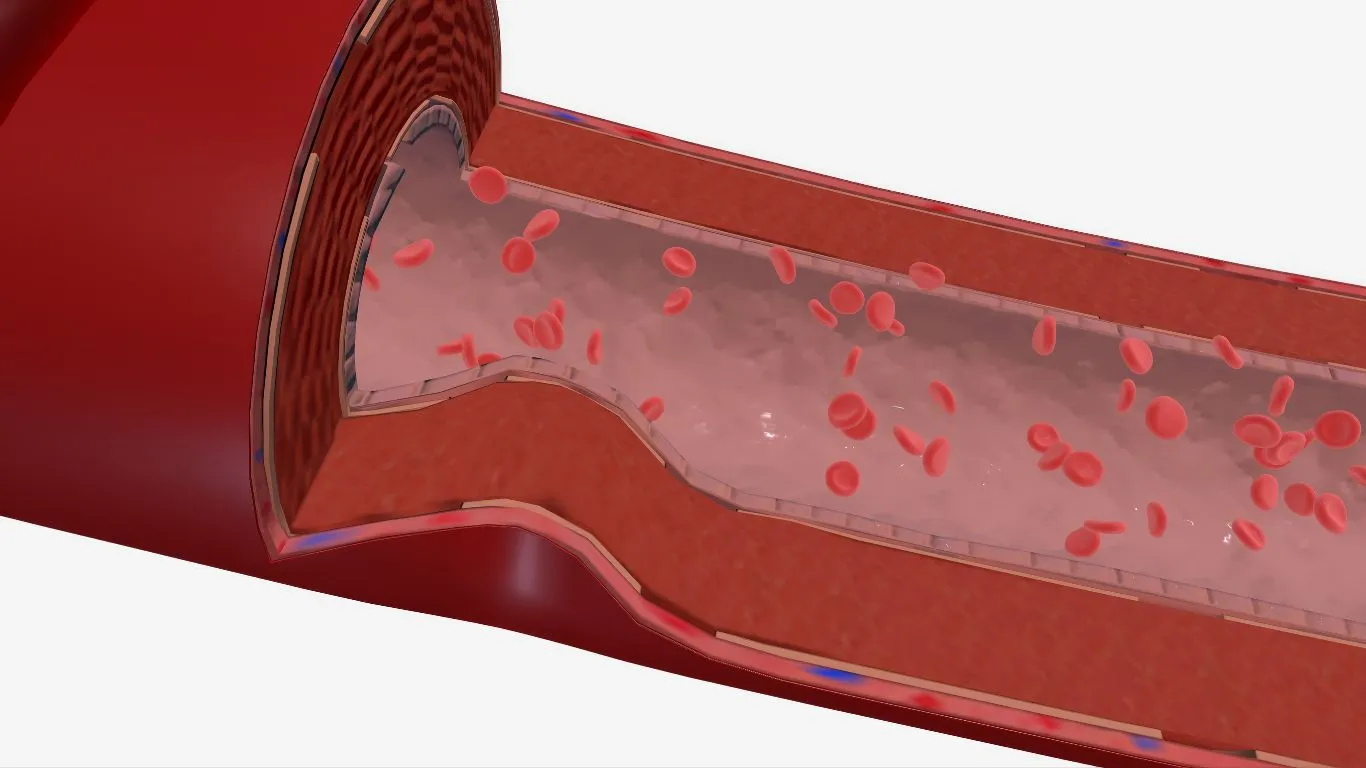
- Narrowing of coronary arteries due to the buildup of a layer of fat on the blood vessel wall.
- Over time, the size of the fatty layer increases, narrowing the arteries, which impedes blood flow. Alternatively, a rupture of a fatty plaque from the blood vessel wall can lead to its blockage and the formation of a blood clot in the heart.
Atrial fibrillation (AF)
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the main causes of blood clotting in the heart, which can be detailed as follows:
- The rapid heartbeat in the heart’s atria leads to ineffective blood pumping, causing blood stagnation and clotting within the heart.
- Blood clots often form in the left atrium in this condition, significantly increasing the risk of these clots traveling from the heart to the brain, potentially causing a stroke.
Coronary artery stenosis
This condition involves the narrowing of arteries responsible for supplying blood to the heart muscle due to muscular contraction. Often of unknown cause, smokers are at increased risk of developing this type of spasm and coronary artery stenosis, which leads to reduced or blocked blood flow, thereby increasing the risk of blood clotting.
Other causes
There are several other factors that may lead to blood clotting in the heart, such as:
- Congenital heart defects.
- Vascular inflammation.
- Heart surgery.
Read More: Treatment of blood clots with catheterization
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of blood clotting in the heart, including:
- Smoking.
- High blood pressure.
- Having type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- High cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Having a family history of arterial sclerosis or heart diseases.
- Frequent exposure to stress and psychological anxiety.
- Following an unhealthy diet.
- Lack of physical exercise or low physical activity.
- Sitting for long periods.
References:
[1] – https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17675-blood-clots
[2] – https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/blood-clots/basics/causes/sym-20050850
[3] – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/what-causes-blood-clots-in-the-heart#causes
[4] – https://www.healthline.com/health/coronary-artery-disease/coronary-thrombosis#about
[5] – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/coronary-thrombosis#symptoms
[6] – https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/arterial-thrombosis/
[7] – https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/atrial-fibrillation/atrial-fibrillation-blood-clots