14 سبتمبر Is Vascular Dilation Dangerous?
Vascular dilation (Aneurysm) is a health issue that can vary in severity depending on its location and the speed of its progression. It involves weakening of the walls of a blood vessel, resulting in a bulge in the vessel wall where blood can accumulate. Often, it does not cause any symptoms or health complications unless the dilation increases significantly or there is pressure on neighboring organs, or if the blood vessel ruptures, which can lead to serious health complications.
Dr. Amir Malkawi, a vascular surgery consultant, will explain in the following article a range of serious complications that may accompany some types of vascular dilation disorders in the body.
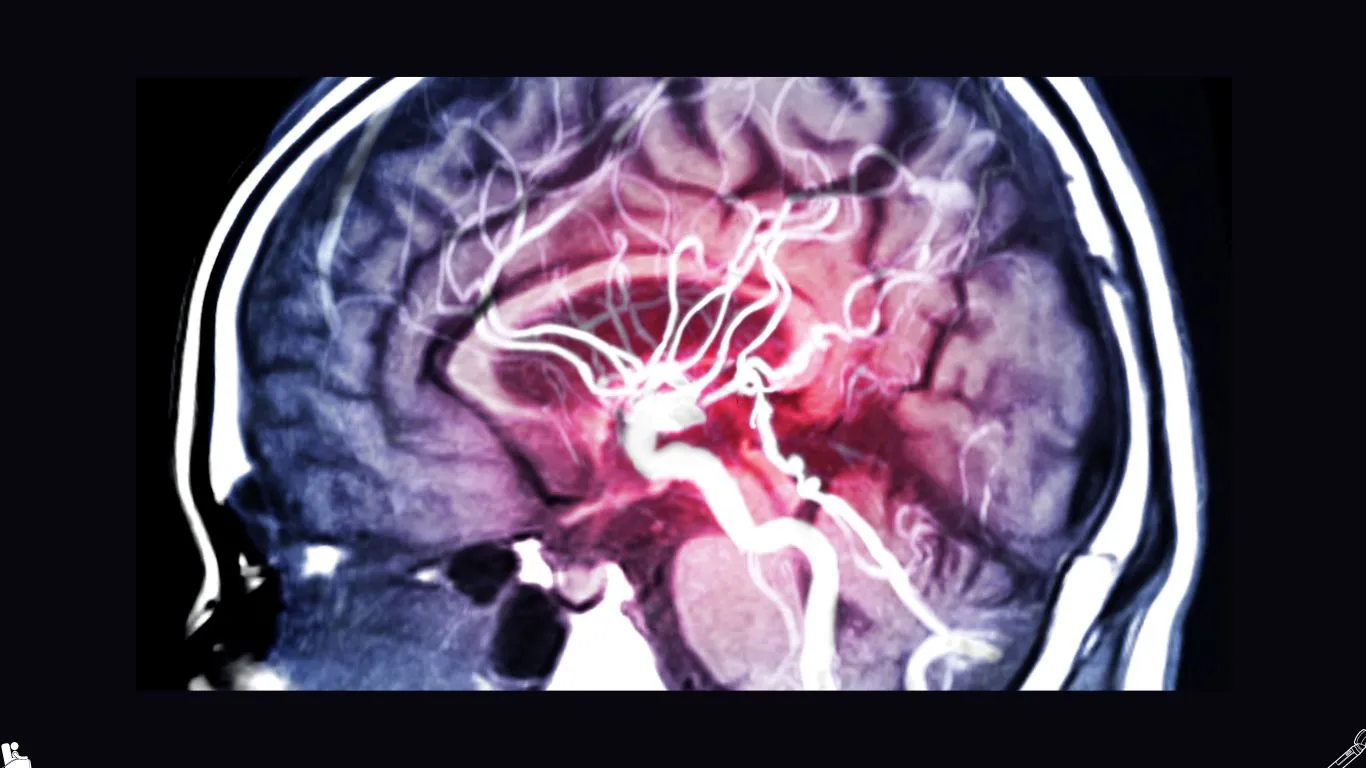
Complications of Vascular Dilation in the Brain
Vascular dilation in the brain can lead to several health complications even before the rupture of the dilated blood vessels. It can exert pressure on nearby nerves in the brain and affect certain bodily functions. In cases where there is a rupture of the dilated blood vessels in the brain, it becomes a serious condition requiring immediate medical intervention.
When a rupture occurs in the dilated blood vessels in the brain, severe bleeding ensues. Although this bleeding often lasts for a limited period, it can damage or cause death to nearby brain nerve cells. Additionally, it increases pressure inside the skull, affecting the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the brain. This may lead to loss of consciousness or even death. Other serious complications of vascular dilation in the brain include:
- Swelling of brain cells due to disturbances in sodium levels, which can lead to permanent brain damage.
- Constriction or narrowing of blood vessels in the brain, potentially causing ischemic stroke.
- Recurrent bleeding in the brain.
- Brain edema or fluid accumulation in the brain, putting pressure on brain cells.
Read Also: The Carotid artery disease and strokes
Complications of Vascular Dilation in the Aorta
Vascular dilation (Aneurysm) can occur in the aorta in the chest or abdominal region. Monitoring of vascular dilation in mild cases is often sufficient to detect the rate of progression of the problem. However, in some cases, immediate medical intervention may be required before a rupture occurs in the dilated aortic wall, as rupture can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Formation of blood clots in the body.
- Severe and serious bleeding that can lead to severe drop in blood pressure and vascular shock.
- Increased risk of stroke.
Complications of Popliteal Artery Aneurysm
Popliteal artery aneurysm affects the wall of the artery behind the knee. It rarely leads to serious health complications because it seldom progresses to the stage of artery rupture. However, in some cases, a blood clot may form in the area of the popliteal artery aneurysm, leading to sudden and acute cessation of blood circulation in the affected leg, resulting in:
- Loss of sensation in the leg.
- Severe tingling and numbness.
- Change in skin color in the area and feeling cold to the touch.
- Inability to feel a pulse when palpating the area behind the knee.
- Inability to move the foot.
It is worth noting that all types of vascular dilation require regular follow-up with a specialist to monitor the condition. Neglecting this or avoiding appropriate treatment should be avoided at all costs to prevent the development of the mentioned health complications, which can threaten the life of individuals affected by vascular dilation. Upon diagnosis of vascular dilation, individuals should work to prevent the progression of the condition through adopting positive lifestyle changes.
Feel free to consult Dr. Amir Malkawi’s clinic, as it is your gateway to enjoying good heart and vascular health, and can assist you in minimizing the risk of serious complications and problems.
References:
[1] – https://www.verywellhealth.com/aneurysm-5181456
[2] – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/156993
[3]-https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/brain-aneurysm/symptoms-causes/syc-20361483
[4] – https://www.verywellhealth.com/aortic-aneurysm-overview-1745744
[5]-https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/thoracic-aortic-aneurysm/symptoms-causes/syc-20350188