17 أغسطس Peripheral Vascular Catheterization
Peripheral vascular catheterization is used to diagnose certain cases of peripheral artery disease, also known as arterial occlusive disease, or to treat severe cases of the disease. Dr. Amir Malkawi, a vascular surgery consultant, will explain all aspects related to peripheral vascular catheterization, including preparations, pre-operative and post-operative instructions in the following article.
Definition of Peripheral Vascular Catheterization
Peripheral vascular catheterization involves using a flexible, thin tube inserted through the skin to reach the affected arteries in the legs. Its purpose is to diagnose issues with the leg arteries, visualize blood vessels in the legs, remove blockages, or widen narrowed arteries in the legs.
Preparing for Peripheral Vascular Catheterization
There are several steps recommended by Dr. Amir Malkawi to prepare for peripheral vascular catheterization, whether it’s for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. These steps include:
- Informing the doctor about all medications being taken, as some medications may need to be stopped before the procedure.
- Informing the doctor about any allergies, even if they are not related to medications, such as food allergies.
- The doctor may ask you to refrain from smoking before the procedure. If you are unable to do so, it’s important to inform the doctor to take appropriate measures.
- Informing the doctor about any recent infections.
- Abstaining from eating or drinking for at least 8 hours before the procedure.
- Informing the doctor if there is any suspicion of pregnancy for women.
- Informing the doctor about any history of bleeding disorders.
Read more: Reducing symptoms of varicose veins without surgery
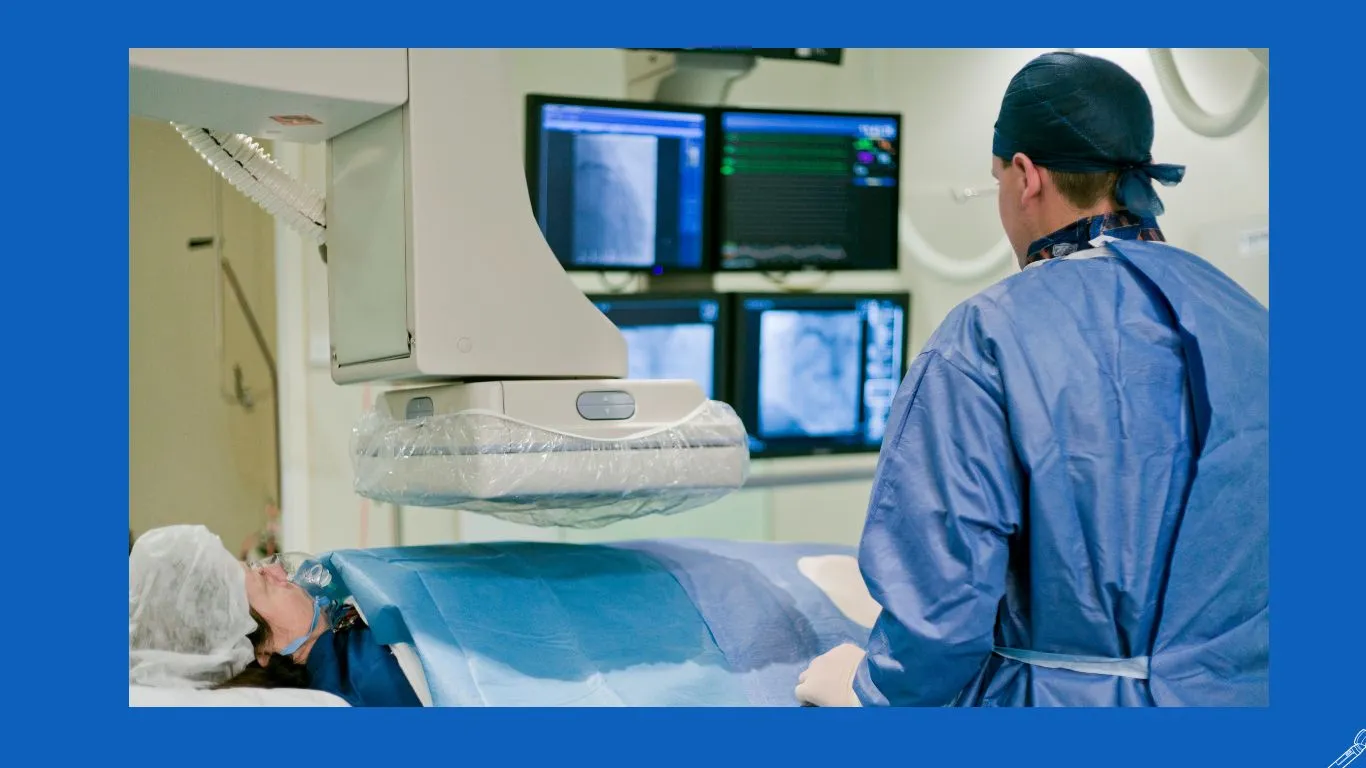
Steps of Peripheral Vascular Catheterization
The procedure takes about an hour or less, and Dr. Amir Malkawi performs peripheral vascular catheterization in the hospital after administering local anesthesia and sedative medications. The person is usually conscious during the procedure. The steps of peripheral vascular catheterization include:
- Inserting the precise and flexible catheter tube through the skin into a major artery. The catheter is then advanced through the arteries to reach the affected artery. It’s important to note that the person does not feel the catheter moving within the arteries due to the absence of sensory nerves in the arteries.
- Inflating the balloon attached to the catheter upon reaching the affected artery to open it up.
- Once at the affected site of the arteries, the doctor may perform imaging of the arteries if the goal is diagnostic, or remove blood clots or place a stent to widen the artery if the goal is treatment.
- Subsequently, the catheter is gently withdrawn, and the procedure site is closed with medical sutures.
Risks
In general, peripheral vascular catheterization is a safe procedure. However, in rare cases, it may be associated with some side effects, including:
- Blood clotting
- Bleeding
- Respiratory disturbances
- Unusual reaction to the contrast dye used for imaging
- Infection
- Arterial tear
Recurrence of blockage in the affected artery
It is important to remember that consulting a skilled and experienced doctor will help mitigate these potential side effects of peripheral vascular catheterization. Therefore, do not hesitate to visit Dr. Amir Malkawi’s clinic for expert care.
Recovery
After peripheral vascular catheterization, the person may experience some discomfort at the catheter insertion site, which typically subsides within a few days. The intensity of discomfort can be reduced with pain relievers. Dr. Amir Malkawi recommends the following post-procedure instructions:
- Change the dressing regularly as per the doctor’s instructions.
- Lie down with gentle pressure on the operation site for half an hour if there is minor bleeding in the area during the recovery phase. However, in case of severe bleeding or bleeding due to heavy lifting or exertion, it is advisable to consult the doctor immediately.
- Inform the doctor immediately if any unusual symptoms occur, such as swelling, redness, or purulent discharge, as they may indicate an infection requiring treatment.
- Elevate the legs as much as possible when sitting or lying down. Several pillows can be placed under the feet to assist with elevation.
- Adhere to the treatment plan and take medications prescribed by the doctor.
- Follow a healthy diet to aid recovery after the procedure and avoid smoking, while engaging in physical activities recommended by the doctor.
References:
[2]-https://www.chinatowncardiology.com/contents/our-services/vascular-procedures/peripheral-procedures
[3]-https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/diagnosing-pad/peripheral-angiogram
[4] – https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007393.htm
[5] –https://www.secondscount.org/treatment/catheter-based-treatment-peripheral-artery-disease
[6] – https://www.healthline.com/health/angioplasty-and-stent-placement-peripheral-arteries